
VDO Biotech’s magnetic microspheres are designed for extraction, purification and detection of biological samples. The high magnetic content and moderate density ensure that the microspheres have fast magnetic response speed and excellent resuspension under the action of a magnetic field, and are suitable for different types of automated instruments.
The microspheres for extraction and purification have a core-shell structure, high magnetic content, large specific surface area, etc., and a large number of functional groups or proteins are coated to the surface.
Magnetic microspheres for detection can be coated with streptavidin on the surface, so that it can specifically bind to biotin. By conjugating biotin to the antibody of interest (or antigen/hapten), these biomolecules can be bound to the surface of the microspheres.
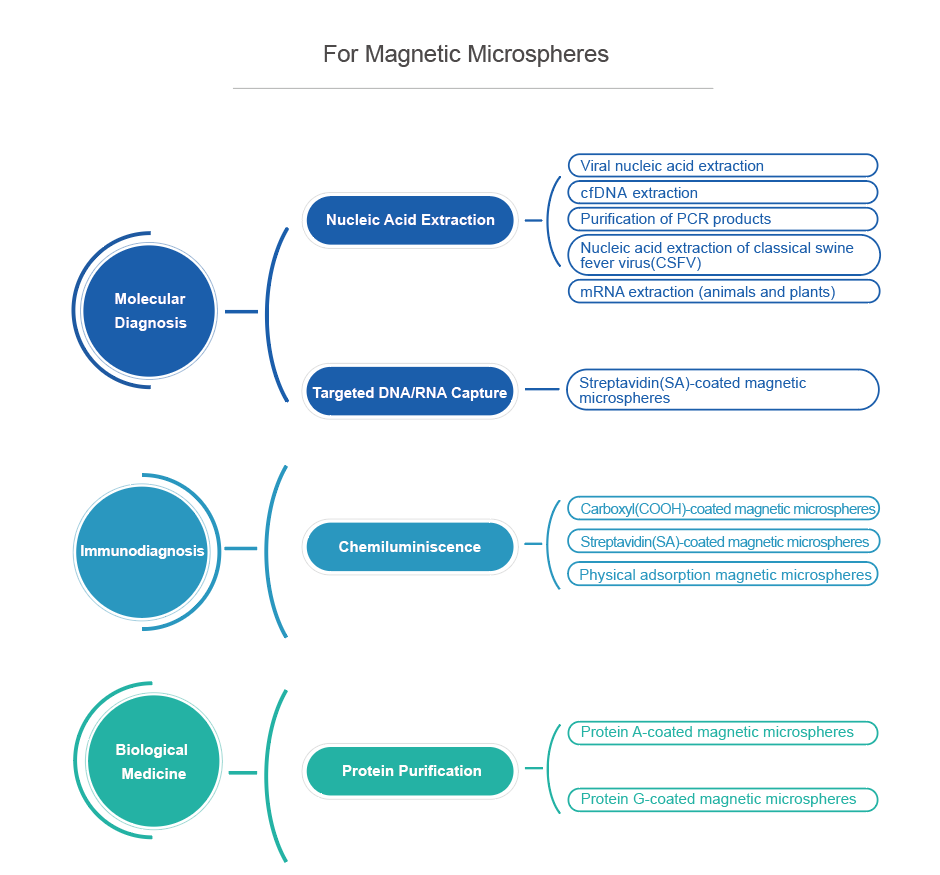
VDO Biotech uses advanced manufacturing processes to provide magnetic microspheres with a variety of functions and specifications for scientific and industrial customers. In addition, we also provide customized magnetic microspheres services according to customers' specific needs.
This series of products can be stored for a long time under appropriate conditions, please refer to the product manual for details. However, operations such as freezing, direct drying, and drying of the product will cause irreversible agglomeration of the microspheres, resulting in a decrease in product performance.
